How to classify transformers
How to classify transformers
Classification and structure of transformers
Transformer classification
Classification by cooling method: dry (self-cooling) transformer, oil immersed (self-cooling) transformer, fluoride (evaporative cooling) transformer.
Classification by moisture-proof mode: open transformer, pot-sealed transformer, sealed transformer.
Classification by core or coil structure: core transformer, shell transformer, ring transformer, metal foil transformer.
The shell transformer core encloses the coil to form a shell; The core of the transformer is mostly in the coil, and only a part is used as a magnetic loop outside the coil.
According to the number of power phase classification: single-phase transformer, three-phase transformer, polyphase transformer.
Classification by use: power transformer, regulator transformer, audio transformer, medium frequency transformer, high frequency transformer, pulse transformer.
Transformer structure
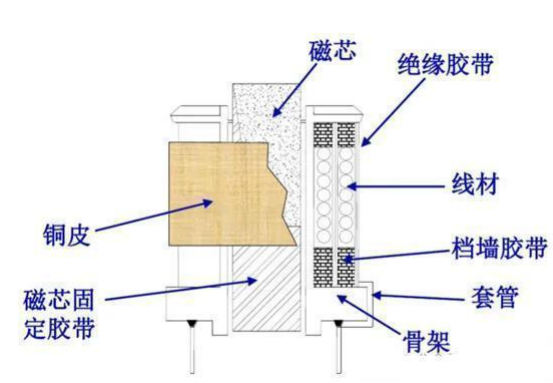
The transformer is mainly composed of: magnetic core, skeleton, enameled wire, tape, sleeve, copper, insulating oil, etc., as shown in the following figure.
1. Core material selection basis:
1, operating frequency range;
2, saturation magnetic density (magnetic induction intensity) size;
3. Loss of magnetic core.
2. Core shape selection basis:
1, power density requirements;
2. Limitations on the height of the finished product;
3, how much winding;
4, the drawing form of enamelled wire. As shown below;
3. Transformer winding, mainly focus on the winding mode and the selection of enameled wire, about the copper wire diameter selection standard in the following details.
【 Go Back 】 | 【 Close this window 】





